Components
What is Mold?
Mold is a hollow form or cavity into which molten plastic is forced to give the shape of the required component.
Molds separate into at least two halves (called the Core and the Cavity) to permit the part to be extracted.
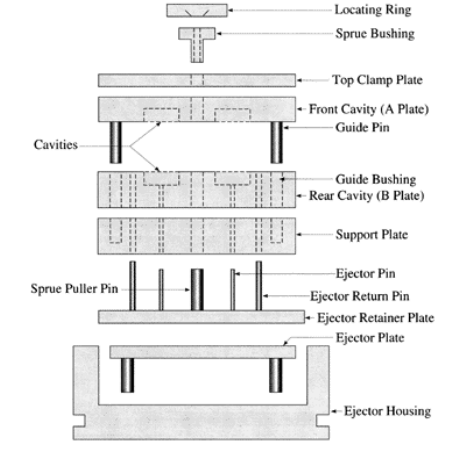
Top Clamping Plate
It holds the fixed side of the mold to the fixed platen of the injection machine.
Locating Ring
A locating ring is a circular member fitted on to the front face of the mold over the sprue bush.
Its purpose is to register (or locate) the mold in the correct position on the injection machine, to ensure proper alignment between the nozzle and the sprue bush, thereby eliminating leakage.
Sprue bushing
A sprue is a channel through which to transfer molten plastic injected from the nozzle of the injector into the mold.
It is a part of sprue bush, which is a separate part from the mold.
Cavity Plate
The plate used to create a cavity (via a gap) that will be filled with the plastic material and form the plastic component.
Core Plate
The section that is engaged in opening / closing movement is called a core plate.
Guide Pillar and Guide Bush
For each cycle, the core and cavity of mold are aligned to ensure quality. This alignment is ensured by guide pillar and guide bush.
Ejector retainer plate
This plate is used to hold the ejector pins, shoulder bolts, and give space to ejector leader pin and support pillar.
Ejector Plate
This plate pushes the ejector pins and return pins to eject the molded product and it is connected with ejector rods and then clamping unit hydraulic system.
Spacer Block
Mounted between the movable clamping plate (bottom plate) and the movable cavity plate to give space and allow the ejector plate to move when ejecting the part.
The required length of spacer block depend on ejector stroke that needed to eject product.
Ejection Pin
A rod, pin or sleeve that pushes a molded part off of a core or out of a cavity of a mold.
Ejector Return Pins
Projections that push the ejector assembly back as the mold closes. Also called surface pins or return pins.
Movable Clamping Plate or Bottom plate
This plate holds the movable side of the mold like spacer block, support plate, cavity plate and ejector mechanism to the movable platen of the injection machine.
